Can Density Be Used to Help Identify a Mixture Vs a Pure Substance
i.ii: Nomenclature of Matter
- Page ID
- 21692
Learning Objectives
- To classify affair.
Chemists written report the structures, concrete backdrop, and chemical properties of cloth substances. These consist of matter , which is anything that occupies space and has mass. Gold and iridium are matter, as are peanuts, people, and postage stamps. Smoke, smog, and laughing gas are affair. Energy, light, and sound, however, are not matter; ideas and emotions are besides not matter.
The mass of an object is the quantity of matter information technology contains. Do non misfile an object's mass with its weight , which is a force caused by the gravitational attraction that operates on the object. Mass is a central belongings of an object that does non depend on its location.In concrete terms, the mass of an object is directly proportional to the force required to modify its speed or direction. A more than detailed discussion of the differences between weight and mass and the units used to measure them is included in Essential Skills 1 (Section ane.nine). Weight, on the other manus, depends on the location of an object. An astronaut whose mass is 95 kg weighs about 210 lb on Earth merely just nearly 35 lb on the moon because the gravitational force he or she experiences on the moon is approximately i-sixth the forcefulness experienced on Globe. For practical purposes, weight and mass are often used interchangeably in laboratories. Because the force of gravity is considered to be the same everywhere on Earth's surface, 2.2 lb (a weight) equals 1.0 kg (a mass), regardless of the location of the laboratory on Earth.
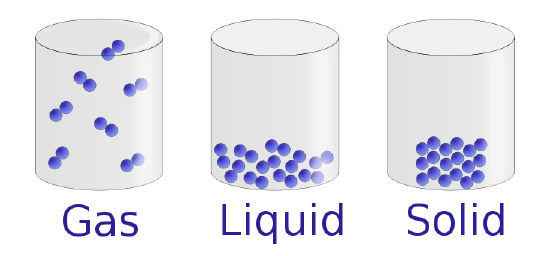
Under normal conditions, there are three distinct states of matter: solids, liquids, and gases. Solids are relatively rigid and have fixed shapes and volumes. A stone, for example, is a solid. In contrast, liquids have stock-still volumes but flow to assume the shape of their containers, such every bit a potable in a can. Gases , such as air in an car tire, have neither fixed shapes nor fixed volumes and expand to completely fill up their containers. Whereas the volume of gases strongly depends on their temperature and pressure (the amount of force exerted on a given area), the volumes of liquids and solids are virtually independent of temperature and force per unit area. Affair can often change from one physical state to some other in a process called a physical change . For example, liquid water can be heated to form a gas called steam, or steam can exist cooled to form liquid water. Withal, such changes of state do not affect the chemic limerick of the substance.
Pure Substances and Mixtures
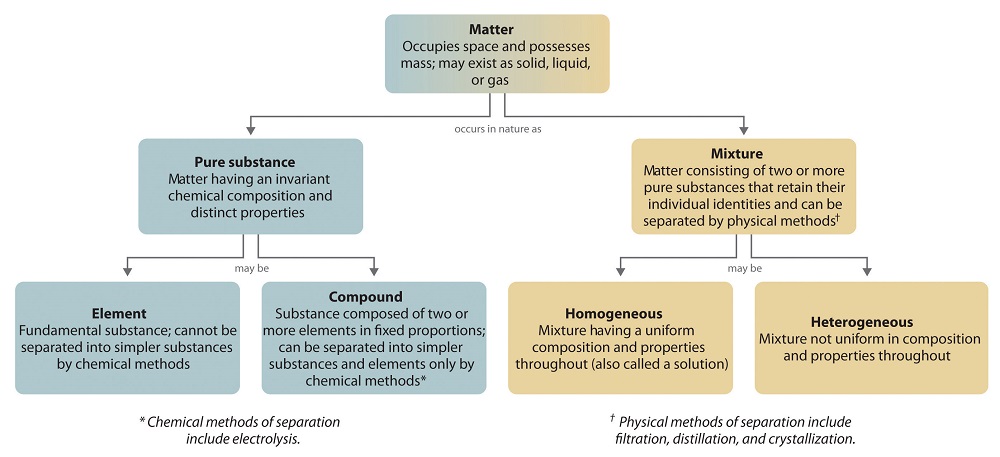
A pure chemical substance is whatever matter that has a fixed chemical limerick and feature properties. Oxygen, for case, is a pure chemical substance that is a colorless, odorless gas at 25°C. Very few samples of thing consist of pure substances; instead, almost are mixtures, which are combinations of two or more pure substances in variable proportions in which the individual substances retain their identity. Air, tap water, milk, blue cheese, bread, and dirt are all mixtures. If all portions of a material are in the same state, have no visible boundaries, and are uniform throughout, and then the fabric is homogeneous . Examples of homogeneous mixtures are the air we breathe and the tap h2o nosotros drink. Homogeneous mixtures are also called solutions. Thus air is a solution of nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, carbon dioxide, and several other gases; tap water is a solution of small amounts of several substances in water. The specific compositions of both of these solutions are not fixed, withal, but depend on both source and location; for example, the limerick of tap water in Boise, Idaho, is non the same as the composition of tap water in Buffalo, New York. Although most solutions we encounter are liquid, solutions can as well be solid. The gray substance still used by some dentists to fill tooth cavities is a circuitous solid solution that contains 50% mercury and 50% of a pulverization that contains mostly silver, tin can, and copper, with pocket-sized amounts of zinc and mercury. Solid solutions of two or more metals are ordinarily called alloys.
If the composition of a textile is not completely compatible, then it is heterogeneous (eastward.g., chocolate chip cookie dough, blue cheese, and clay). Mixtures that appear to be homogeneous are often constitute to be heterogeneous later microscopic test. Milk, for example, appears to be homogeneous, just when examined under a microscope, it clearly consists of tiny globules of fat and protein dispersed in water. The components of heterogeneous mixtures can usually be separated by simple means. Solid-liquid mixtures such equally sand in water or tea leaves in tea are readily separated by filtration, which consists of passing the mixture through a barrier, such as a strainer, with holes or pores that are smaller than the solid particles. In principle, mixtures of ii or more than solids, such as sugar and table salt, can exist separated by microscopic inspection and sorting. More complex operations are usually necessary, though, such as when separating gold nuggets from river gravel by panning. Offset solid material is filtered from river water; then the solids are separated by inspection. If gold is embedded in stone, it may accept to be isolated using chemical methods.
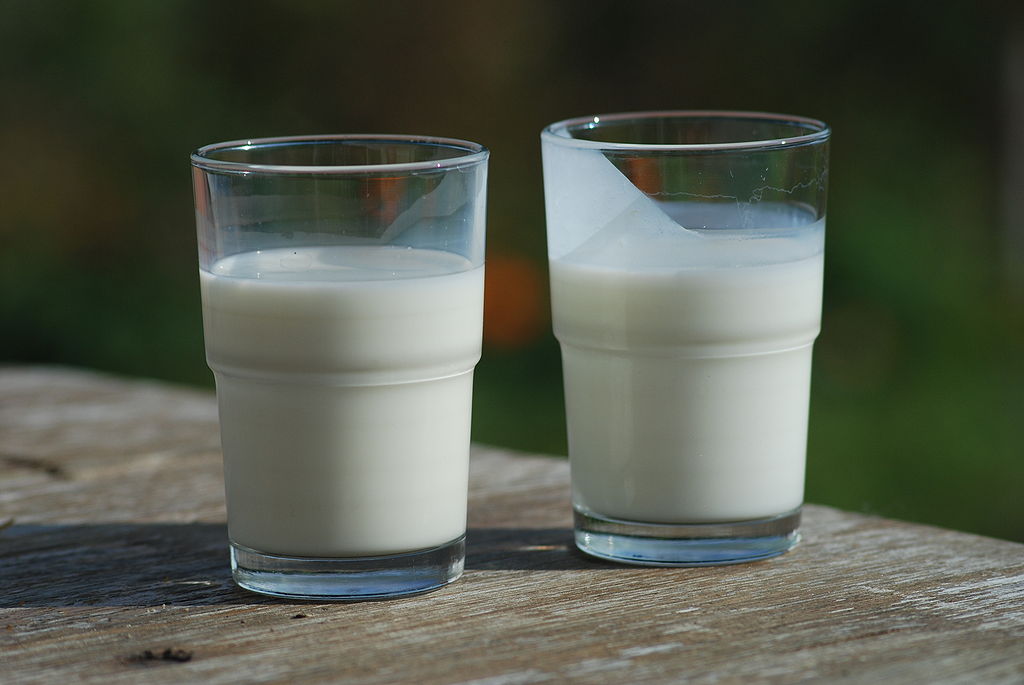-and-Milk-(left).jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=454&height=303)
Homogeneous mixtures (solutions) can be separated into their component substances past physical processes that rely on differences in some physical property, such as differences in their boiling points. Two of these separation methods are distillation and crystallization. Distillation makes apply of differences in volatility, a measure of how easily a substance is converted to a gas at a given temperature. A unproblematic distillation appliance for separating a mixture of substances, at to the lowest degree 1 of which is a liquid. The most volatile component boils beginning and is condensed back to a liquid in the h2o-cooled condenser, from which it flows into the receiving flask. If a solution of salt and water is distilled, for instance, the more volatile component, pure water, collects in the receiving flask, while the salt remains in the distillation flask.
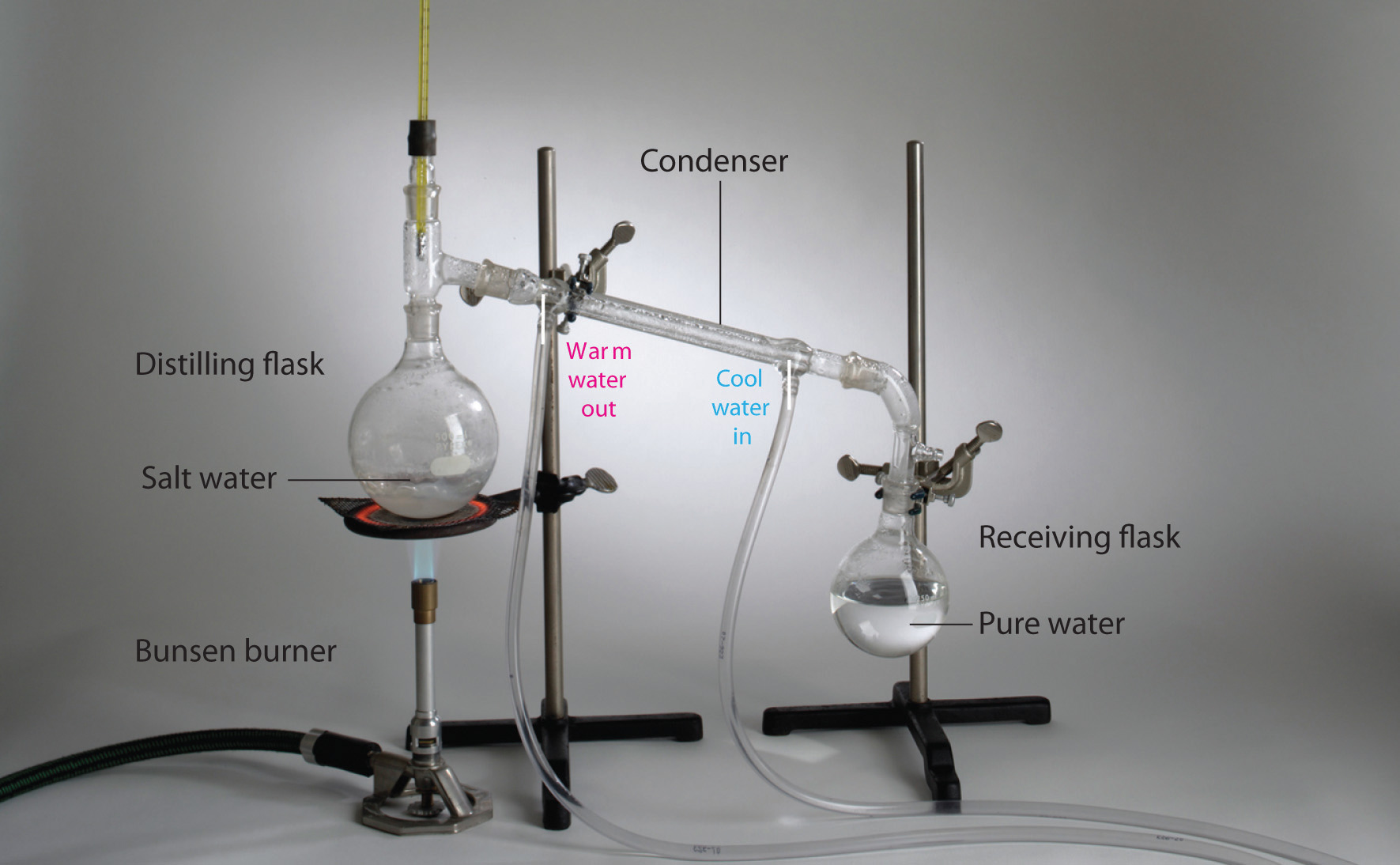

Mixtures of ii or more than liquids with different boiling points tin can be separated with a more complex distillation apparatus. I example is the refining of crude petroleum into a range of useful products: aviation fuel, gasoline, kerosene, diesel fuel, and lubricating oil (in the approximate club of decreasing volatility). Another example is the distillation of alcoholic spirits such as brandy or whiskey. (This relatively simple procedure caused more than a few headaches for federal authorities in the 1920s during the era of Prohibition, when illegal stills proliferated in remote regions of the Us!)
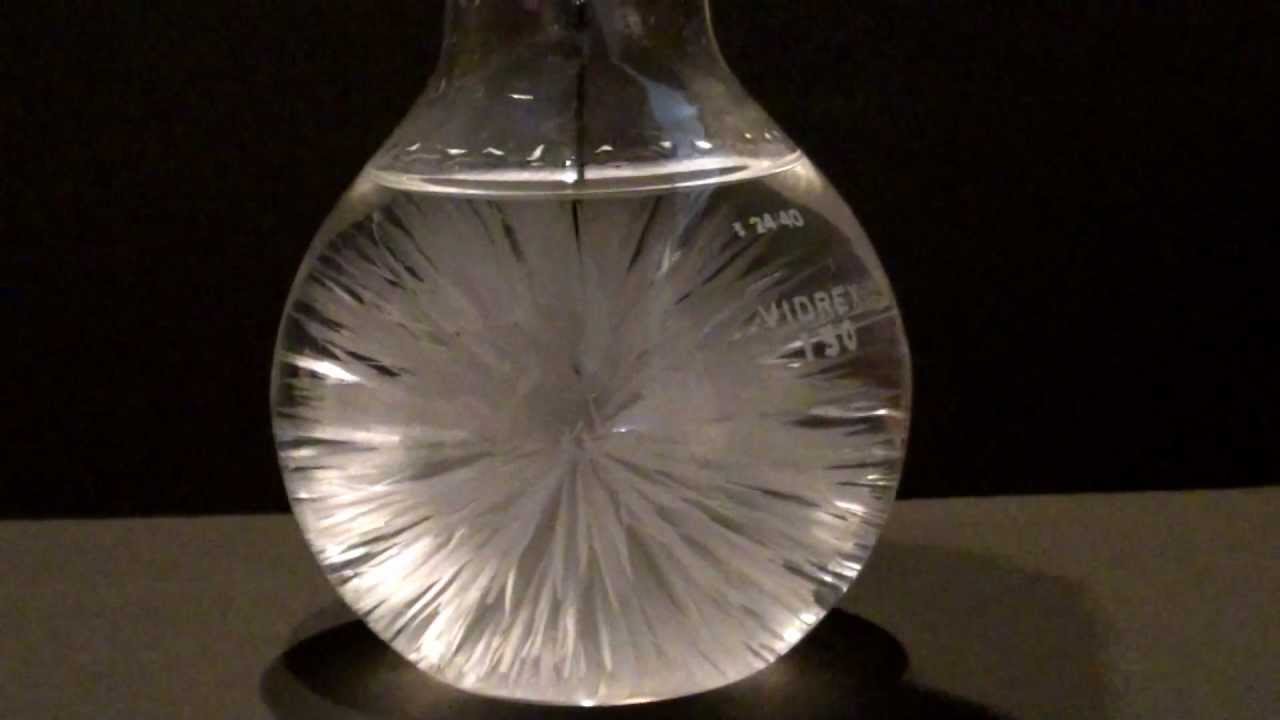
Crystallization separates mixtures based on differences in solubility, a measure of how much solid substance remains dissolved in a given amount of a specified liquid. Well-nigh substances are more soluble at higher temperatures, so a mixture of two or more substances can be dissolved at an elevated temperature so immune to absurd slowly. Alternatively, the liquid, chosen the solvent, may be immune to evaporate. In either case, the least soluble of the dissolved substances, the ane that is least likely to remain in solution, usually forms crystals first, and these crystals can be removed from the remaining solution by filtration.

Nearly mixtures can be separated into pure substances, which may be either elements or compounds. An element , such as gray, metallic sodium, is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler ones by chemical changes; a compound , such as white, crystalline sodium chloride, contains two or more than elements and has chemical and physical backdrop that are ordinarily unlike from those of the elements of which it is composed. With only a few exceptions, a particular compound has the aforementioned elemental composition (the aforementioned elements in the aforementioned proportions) regardless of its source or history. The chemical composition of a substance is altered in a procedure chosen a chemical change . The conversion of two or more elements, such as sodium and chlorine, to a chemic chemical compound, sodium chloride, is an example of a chemic change, often chosen a chemical reaction. Currently, nigh 118 elements are known, merely millions of chemical compounds take been prepared from these 118 elements. The known elements are listed in the periodic table.
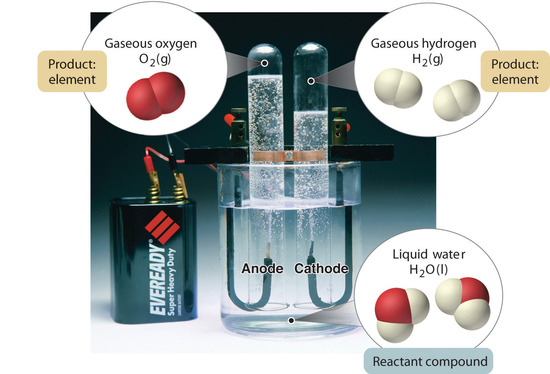
Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\): The Decomposition of Water to Hydrogen and Oxygen by Electrolysis. Water is a chemical compound; hydrogen and oxygen are elements.
Different Definitions of Matter: https://youtu.be/qi_qLHc8wLk
In full general, a reverse chemical procedure breaks downwards compounds into their elements. For example, water (a compound) can be decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen (both elements) by a process called electrolysis. In electrolysis, electricity provides the energy needed to separate a compound into its constituent elements (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). A similar technique is used on a vast scale to obtain pure aluminum, an chemical element, from its ores, which are mixtures of compounds. Because a great bargain of energy is required for electrolysis, the cost of electricity is by far the greatest expense incurred in manufacturing pure aluminum. Thus recycling aluminum is both cost-constructive and ecologically sound.
The overall system of affair and the methods used to separate mixtures are summarized in Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\).
Example \(\PageIndex{one}\)
Identify each substance as a compound, an chemical element, a heterogeneous mixture, or a homogeneous mixture (solution).
- filtered tea
- freshly squeezed orange juice
- a compact disc
- aluminum oxide, a white powder that contains a 2:3 ratio of aluminum and oxygen atoms
- selenium
Given: a chemical substance
Asked for: its nomenclature
Strategy:
- Decide whether a substance is chemically pure. If it is pure, the substance is either an element or a compound. If a substance tin be separated into its elements, it is a compound.
- If a substance is non chemically pure, it is either a heterogeneous mixture or a homogeneous mixture. If its composition is uniform throughout, it is a homogeneous mixture.
Solution
- A Tea is a solution of compounds in water, and then it is not chemically pure. It is usually separated from tea leaves by filtration. B Because the composition of the solution is compatible throughout, it is a homogeneous mixture.
- A Orange juice contains particles of solid (pulp) as well as liquid; it is not chemically pure. B Because its composition is not uniform throughout, orange juice is a heterogeneous mixture.
- A A compact disc is a solid material that contains more than 1 element, with regions of different compositions visible along its edge. Hence a meaty disc is non chemically pure. B The regions of different composition indicate that a compact disc is a heterogeneous mixture.
- A Aluminum oxide is a single, chemically pure compound.
- A Selenium is ane of the known elements.
Practice \(\PageIndex{one}\)
Identify each substance as a chemical compound, an element, a heterogeneous mixture, or a homogeneous mixture (solution).
- white wine
- mercury
- ranch-style salad dressing
- table sugar (sucrose)
- Reply A
-
solution
- Answer B
-
chemical element
- Respond C
-
heterogeneous mixture
- Answer D
-
compound
Different Definitions of Changes: https://youtu.be/OiLaMHigCuo
Summary
Affair can be classified according to concrete and chemic properties. Matter is annihilation that occupies space and has mass. The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. A concrete modify involves the conversion of a substance from ane state of matter to another, without irresolute its chemical composition. Most matter consists of mixtures of pure substances, which can be homogeneous (uniform in composition) or heterogeneous (unlike regions possess unlike compositions and backdrop). Pure substances tin be either chemical compounds or elements. Compounds can be cleaved down into elements past chemical reactions, simply elements cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical ways. The properties of substances can be classified equally either physical or chemical. Scientists tin observe physical properties without irresolute the composition of the substance, whereas chemical properties describe the trend of a substance to undergo chemical changes (chemical reactions) that modify its chemic limerick. Physical backdrop can be intensive or extensive. Intensive backdrop are the same for all samples; exercise non depend on sample size; and include, for case, color, concrete state, and melting and boiling points. Extensive properties depend on the corporeality of material and include mass and volume. The ratio of ii extensive properties, mass and book, is an important intensive property chosen density.
miesnerlegiring76.blogspot.com
Source: https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/General_Chemistry/Map%3A_Chemistry_-_The_Central_Science_(Brown_et_al.)/01._Introduction%3A_Matter_and_Measurement/1.2%3A_Classification_of_Matter
0 Response to "Can Density Be Used to Help Identify a Mixture Vs a Pure Substance"
Post a Comment